89 MDS: Dyserythropoiesis, Dysmyelopoiesis & Dysmegakaryopoiesis
Michelle To and Valentin Villatoro
As previously discussed, MDS is a clonal disorder that results in defective cell maturation and results in dysplastic changes. The dysplasia can be seen in both the peripheral blood and in the bone marrow. Dysplasia may be seen in one or more cell lines, and the types of dysplasia seen vary. Below are descriptions that may be seen, organized by cell lineage.
Dyserythropoiesis
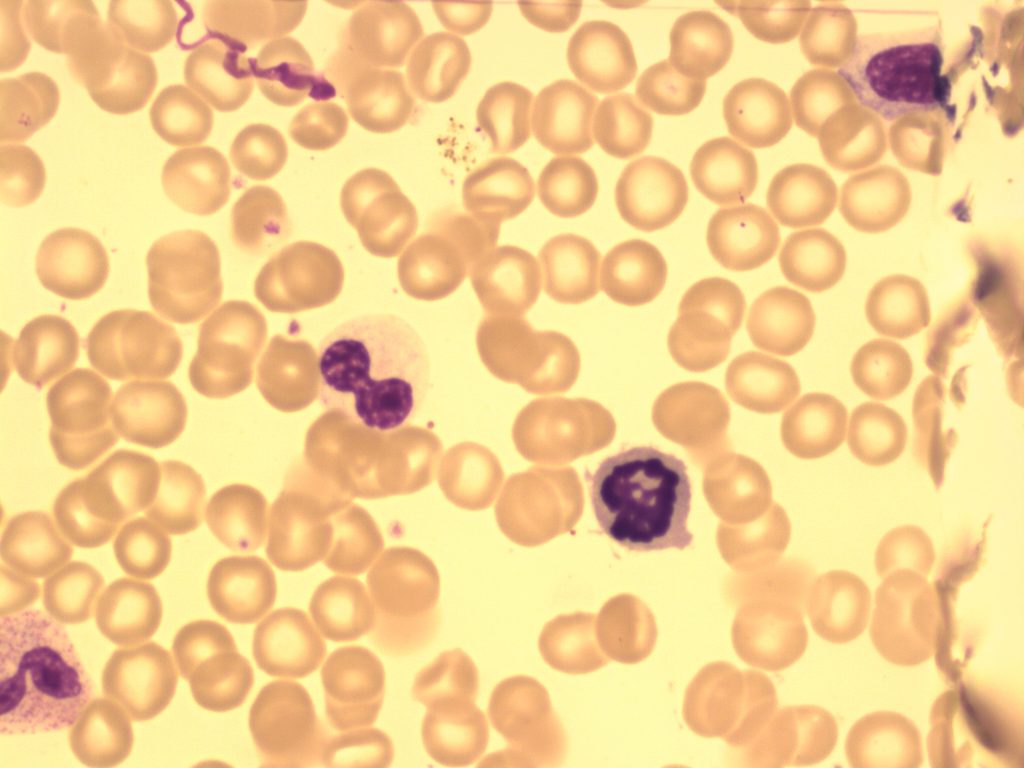
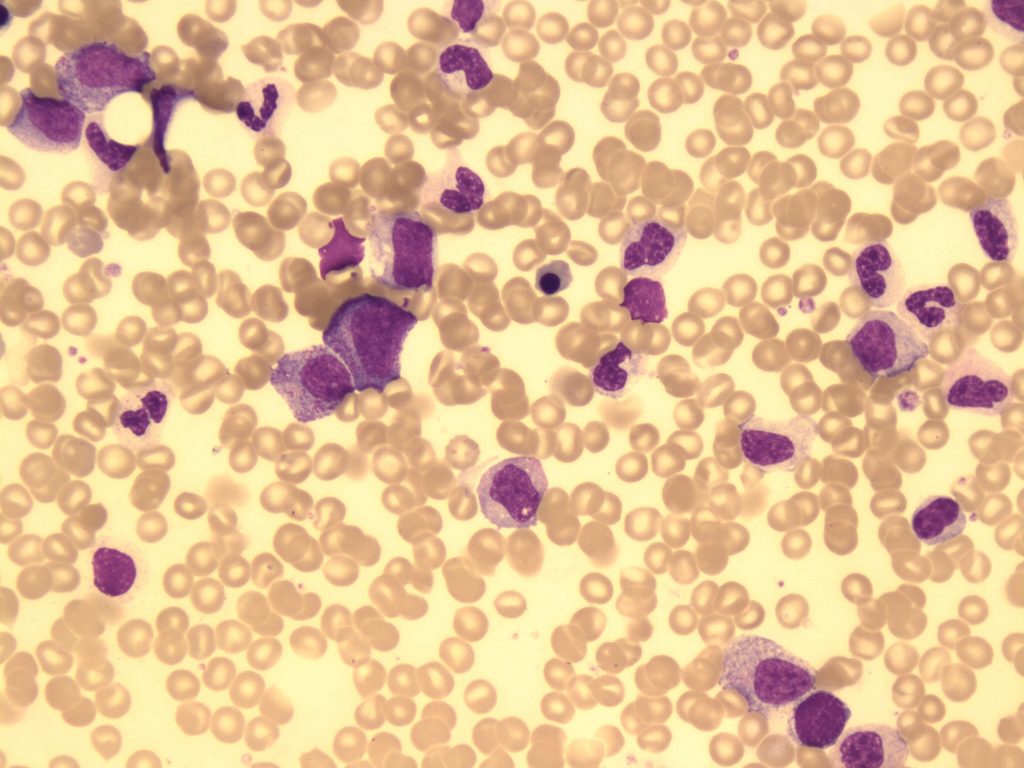
- An image from a bone marrow smear showing a hypogranular, hyposegmented neutrophil (center-left) and a mitotic figure that appears to be an erythroid precursor (center-right) seen in myelodysplastic syndrome. 100x oil immersion. From MLS Collection, University of Alberta, https://doi.org/10.7939/R34M91S2D
Affected Cell line: Erythroids.1-3
Table 1. Dysplastic features found in MDS erythrocytes in the peripheral blood and bone marrow.1-3
|
PBS: Dimorphic Population Oval-macrocytes Hypochromic/Microcytic RBCs (with normal iron stores) Basophilic stippling Howell-Jolly bodies Siderocytes Decreased polychromasia |
BM: Multiple Nuclei Abnormal Nuclear shapes (budding, lobes, fragmentation, bridging) Megaloblastoid features Vacuolization Ringed Sideroblasts Abnormal staining of the cytoplasm (due to basophilic stippling and hemoglobin) |
Dysmyelopoiesis/Dysgranulopoiesis
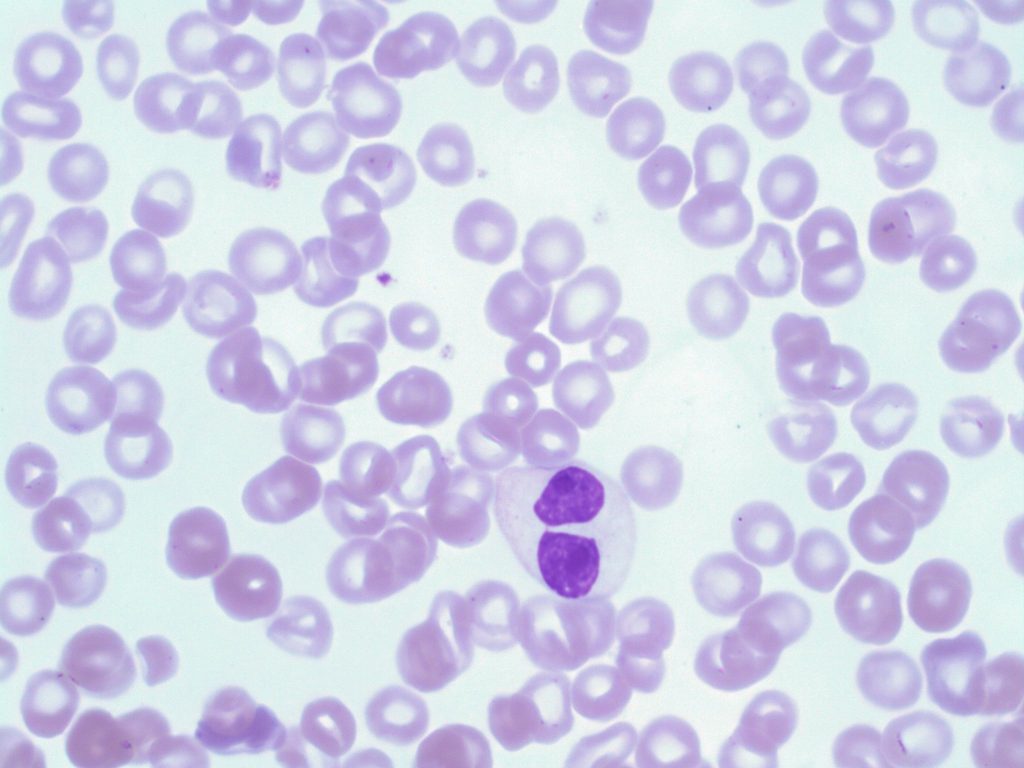
- An image from a peripheral blood smear demonstrating a hyposegmented neutrophil with mature chromatin pattern and hypogranulation seen in a patient with MDS. 100x oil immersion. From MLS Collection, University of Alberta, https://doi.org/10.7939/R3251G157
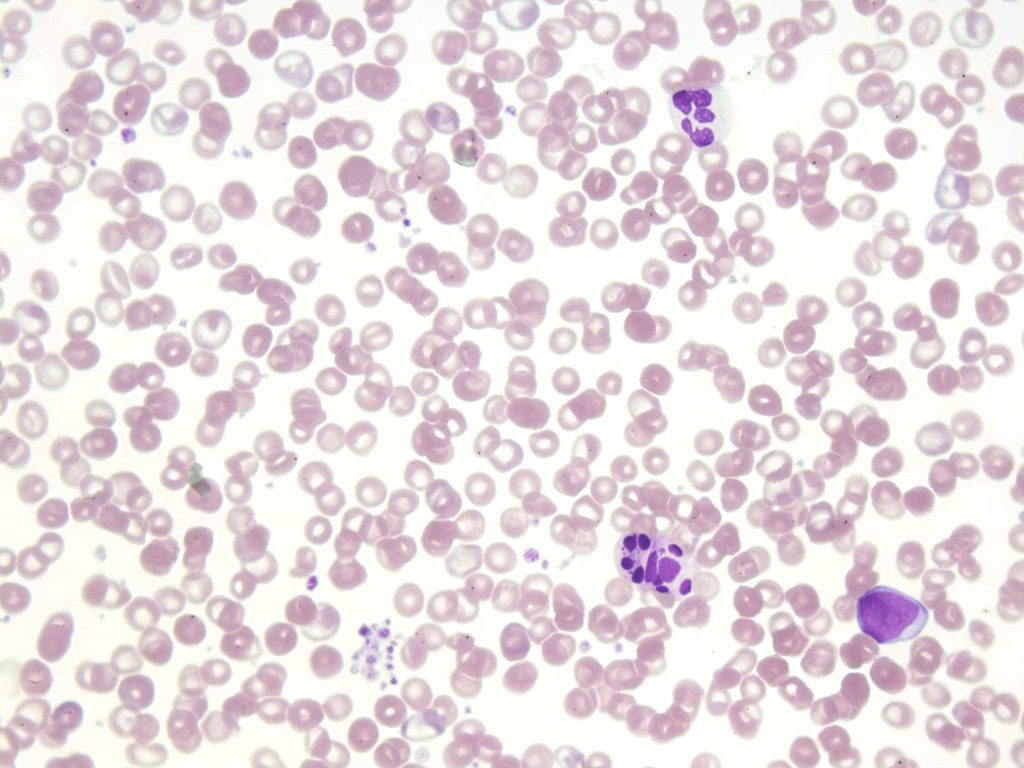
- An image from a peripheral blood smear demonstrating dysplastic features: a neutrophil (top) with hypersegmention and hypogranulation, two neutrophils (bottom-right) undergoing karyorrhexis, and platelet clumping (bottom-left) seen in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. 50x oil immersion. From MLS Collection, University of Alberta, https://doi.org/10.7939/R3BK1750B
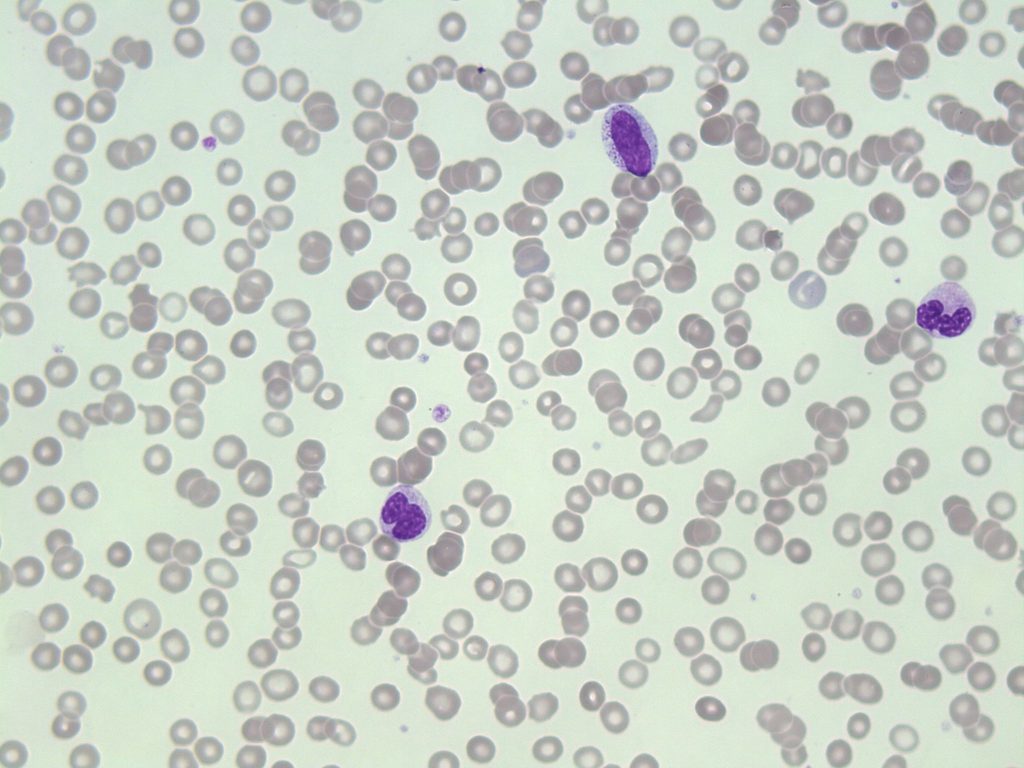
- An image from a peripheral blood smear showing hyposegmented neutrophils and a myeloid precursor seen in myelodysplastic syndrome. 50x oil immersion. From MLS Collection, University of Alberta, https://doi.org/10.7939/R3KP7V654
- An image from a bone marrow smear showing hypogranular neutrophils and hypogranular myeloid precursors seen in myelodysplastic syndrome. 50x oil immersion. From MLS Collection, University of Alberta, https://doi.org/10.7939/R38C9RK5P
Affected Cell line: Granulocytes.1-3
Table 2. Dysplastic features found in MDS granulocytes in the peripheral blood and bone marrow. 1-3
|
PBS: Agranulation Hypogranulation Abnormal nuclear shapes (hypersegmentaion, hyposegmentation, ring-shaped nuclei) Left shift Monocytosis Neutropenia Increased Blasts |
BM: Nuclear-cytoplasmic asynchrony Abnormal cytoplasmic staining Abnormal granulation (hypogranulation, hypergranulation) Increased Blasts +/- Auer rods |
Dysmegakaryopoiesis
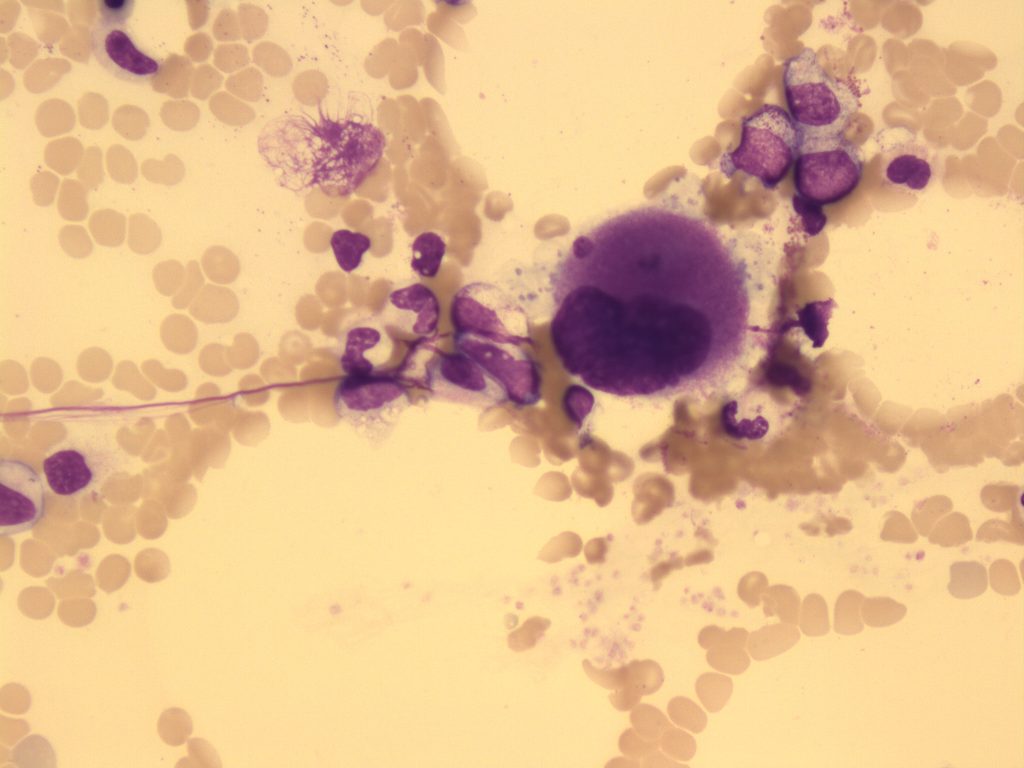
- An image from a bone marrow smear showing mononuclear megakaryocyte seen in myelodysplastic syndrome. 50x oil immersion. From MLS Collection, University of Alberta, https://doi.org/10.7939/R3D21S081
Affected Cell line: Megakaryoctyes and platelets.1-3
Table 3. Dysplastic features found in MDS megakaryocytes and platelets in the peripheral blood and bone marrow. 1-3
|
PBS: Thrombocytopenia Hypogranulation/Agranulation Micromegakaryocytes Giant PLTs |
BM: Magakaryocytes with multiple separated nuclei Abnormal granulation (hypogranulation) Large mononuclear megakaryocytes Micromegakaryocytes Micromegakaryoblasts |
|
Other Tests: Platelet function tests are abnormal |
|
References:
1. Rodak BF. Myelodysplastic syndromes. In: Rodak’s hematology clinical applications and principles. 5th ed. St. Louis, Missouri: Saunders; 2015. p.591-603.
2. Lawrence LW, Taylor SA. Myelodysplastic syndromes. In: Clinical laboratory hematology. 3rd ed. New Jersey: Pearson; 2015. p. 479-99.
3. D’Angelo G, Mollica L, Hebert J, Busque L. Myelodysplastic syndromes. In: Clinical hematology and fundamentals of hemostasis. 5th ed. Philadelphia: F.A. Davis Company; 2009. p. 412-39.