Chapter 4: Statutory and Non-Statutory Deductions
4.4 Income Tax
4.4.1 Income Tax in Canada
Canada, like most countries in the world, taxes personal income. Income tax is a portion of an individual’s or business’s income that is paid to a government to fund government operations and public programs and services. The amount of tax paid varies by jurisdiction and, in most jurisdictions in Canada, varies by the amount of the taxpayer’s income. Typically, someone earning $200,000 per year will be in a higher tax bracket than someone earning $30,000 per year, meaning that the higher income earner will pay a higher rate of tax (that is, a higher percentage of their income and not just a higher absolute amount).
Employers are responsible, under the Income Tax Act, for correctly determining the amount of each employee’s income tax payable to federal and provincial governments (except Québec). Employee tax rates are determined by where each employee reports to work (in-person work) or where the employer is headquartered (remote work) (Government of Canada, 2023). Payroll calculates the amount of income tax to withhold from each employee for each pay period. If payroll software is used, the software will calculate the amount of income tax to be withheld; however, payroll personnel should verify that the tax rates are accurate and understand what the software is doing.
To calculate income tax for a pay period, payroll will need to determine gross taxable income, then subtract the employee’s personal tax credits and deductions to determine net taxable income. Income tax rates for the employee can then be determined and applied.
|
Step |
Instructions |
|
Step 1 |
Calculate the employee’s gross taxable earnings for the pay period based on annual calculation of earnings Gross Taxable Earnings = Gross Income + Taxable Benefits and Allowances for the pay period |
|
Step 2 |
Determine and add up the following amounts for each employee: union dues, employee pension contributions, and any amounts listed on the employee’s TD1 forms (Personal Tax Credits Return); there are both provincial and federal TD1 forms. |
|
Step 3 |
Divide the result of Step 2 by the number of pay periods. |
|
Step 4 |
Subtract the result of Step 3 from Step 1 to determine the employee’s net taxable earnings for the pay period. |
|
Step 5 |
Apply the correct tax rate to the employee’s net taxable earnings. |
The CRA online payroll calculator can be used to determine the amount of income tax withholding for an employee without software or to verify that payroll software is deducting the correct amount from an employee’s pay.
4.4.1.1 Income Tax Calculation Using PDOC
The CRA online payroll calculator is abbreviated as “PDOC.” The calculator can be found here: Payroll Deductions Online Calculator
To begin, accept the terms of using the calculator:
Next, select the type of calculation. The first option, Salary is what is commonly used.
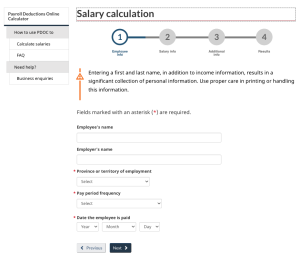
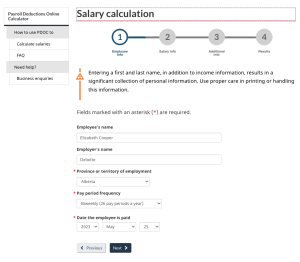
Next, enter the employee and employer information. It is important to select the appropriate province as this will impact the calculation of provincial income tax. The pay period frequency will be likely biweekly, semi-monthly, or monthly, but there are other choices as well. It is also important to note the date the employee is paid and ensure that the correct year is selected. The year selected will determine the rates for CPP, EI, and income tax; these rates typically change each year.
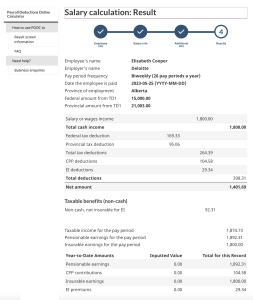
Income Tax Calculation Using PDOC Example
Elizabeth Cooper works for Deloitte in Edmonton, Alberta. She works full-time and is paid $1,800 biweekly. She receives a monthly automobile allowance of $300, which has been determined as reasonable because it is based on CRA rates. Her employer also pays her life insurance premiums of $200 per month.
Elizabeth is not a unionized employee, and she does not participate in an employer pension plan.
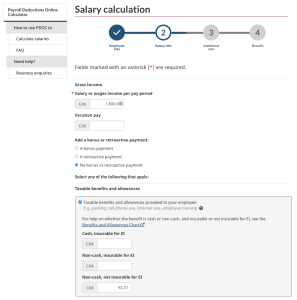
Identify whether there are any taxable benefits:
In the above example, Elizabeth’s life insurance premium is taxable. The vehicle allowance, which is a reasonable allowance as determined by the CRA, is not taxable.
For the taxable benefits, convert monthly amounts to biweekly amounts:
Life insurance: $200 per month × 12 months = $2,400 per year/26 pay periods = $92.31 per pay period
Enter this information in the online payroll calculator (Step 2) to determine her net pay.
First, enter Elizabeth’s salary, then select Taxable benefits and allowances. Enter the amount(s) of the taxable benefit(s) for the pay period. Cash benefits should be entered under Cash, insurable for EI. Recall that non-cash taxable benefits are generally not considered part of insurable earnings. The taxable benefit in the example (life insurance) should be entered as Non-cash, not insurable for EI.
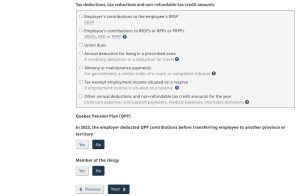
Next, enter the claim code for the employee. There are two options to select from: the first option is the amount from the TD1 form and the second option is the claim code number. If no information is provided, then select Claim Code 1 or allow the calculator to continue with the default, which is the first option. This would be the minimum claim code. For this example, select TD1 form.
Claim codes can be found here: Payroll Deductions Supplementary Tables: Claim codes
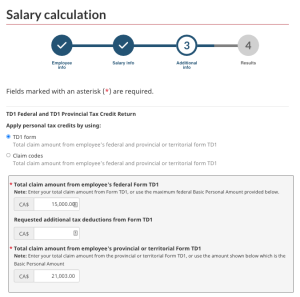
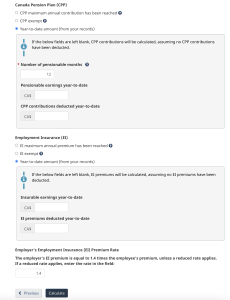
The last step is to click on Calculate to get the CPP, EI, and income tax deductions for the employee, as seen below:
4.4.1.2 Income Tax Calculation Using Payroll Deductions Table
Income tax can also be calculated manually by 1) determining net taxable earnings, then 2) applying the current year’s payroll deductions table for the applicable jurisdiction. The payroll deductions tables for 2023 can be found here: T4032 Payroll Deductions Tables
References
Government of Canada. (2024). Payroll deductions online calculator. https://www.canada.ca/en/revenue-agency/services/e-services/e-services-businesses/payroll-deductions-online-calculator.html
Government of Canada. (2023a). Payroll deductions supplementary tables – In Canada beyond the limit of any province/territory or outside Canada: Claim codes. https://www.canada.ca/en/revenue-agency/services/forms-publications/payroll/t4008-payroll-deductions-supplementary-tables/t4008oc-jan/t4008oc-january-general-information.html#_Toc334772403
Government of Canada. (2023b). Set up and manage employee payroll information: Determine the province of employment (POE). https://www.canada.ca/en/revenue-agency/services/tax/businesses/topics/payroll/set-up-new-employee/determine-province-employment.html
Government of Canada. (2023c). T4032. Payroll deductions tables. https://www.canada.ca/en/revenue-agency/services/forms-publications/payroll/t4032-payroll-deductions-tables.htmll
Image Credits (images are listed in order of appearance)
Government of Canada. (2023). Payroll deductions online calculator: Use the calculator [Screenshot]. https://www.canada.ca/en/revenue-agency/services/e-services/digital-services-businesses/payroll-deductions-online-calculator.html
Government of Canada. (2024). Payroll deductions online calculator: Calculation type [Screenshot]. https://apps.cra-arc.gc.ca/ebci/rhpd/beta/entry
Government of Canada. (2024). Payroll deductions online calculator: Salary calculation step 1 [Screenshot]. https://apps.cra-arc.gc.ca/ebci/rhpd/beta/step1
Government of Canada. (2024). Payroll deductions online calculator: Salary calculation step 1 with information entered [Screenshot]. https://apps.cra-arc.gc.ca/ebci/rhpd/beta/step1
Government of Canada. (2024). Payroll deductions online calculator: Salary calculation step 2 with information entered [Screenshot]. https://apps.cra-arc.gc.ca/ebci/rhpd/beta/step2
Government of Canada. (2024). Payroll deductions online calculator: Salary calculation step 3 with information entered [Screenshot]. https://apps.cra-arc.gc.ca/ebci/rhpd/beta/step3
Government of Canada. (2024). Payroll deductions online calculator: Salary calculation result [Screenshot]. https://apps.cra-arc.gc.ca/ebci/rhpd/beta/results